
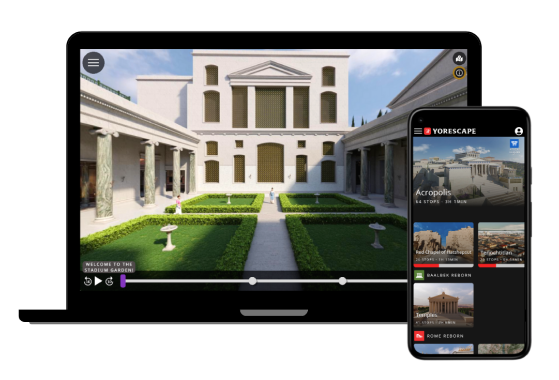
In this tour, you will learn about the Agora, the marketplace of ancient Athens. You will learn about the marketplace, civic buildings, religious sites, and more.
Read More
- Description
- Languages
- Credits
- Bibliography
The Agora is typically described as the central public square and marketplace of ancient Athens, but in reality it was much more than that. The open space used by sellers of goods and services was surrounded by public structures of varying size and architectural and decorative sophistication which served essential civic functions of administration, communication, commemoration, religious activity, and spatial organization. The virtual tour features approximately 40 sites and monuments ranging in date from about 500 to 150 BCE, as well as numerous inscriptions and sculptures. The notional date of the virtual tour is the year 100 BCE, at the end of Athens’ history as an independent city-state and before modification of the Agora under Roman rule. Like the other tour in the Athens Reborn series, the Acropolis, the virtual tour of the Agora was created with the collaboration of the American School of Classical Studies at Athens. In fact, the contents of the tour are drawn mostly from the American School’s excavations in the Agora, which have been running since 1931.
Audio: English
Subtitles: English
Producer:
Bernard Frischer
Project Manager:
Alberto Prieto
Tour Guide/Narration:
Alberto Prieto
Scientific Advisors:
Jenifer Neils
Chavdar Tzochev
Script:
Alberto Prieto
3D Modeling:
Lasha Tshkondia
Art Direction:
Mohamed Abdelaziz
Contributors:
Robert Pitt
Andrew F. Stewart
Image Credits:
The panoramic photographs of the Agora are reproduced with the permission of the Hellenic Ministry of Culture and Sports.
The photograph of the marble votive relief dedicated to a hero (gift of Joseph V. Noble, 1957 57.42) is courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The photograph of the column-krater depicting cavalry (Rogers Fund, 1907 07.286.65) is courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The photographs of Panathenaic amphorae (Rogers Fund, 1914 14.130.12, 1907 07.286.80, and 1916 16.71; Fletcher Fund, 1956 56.171.4) are courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The photograph of the neck-amphora depicting hoplites (Edward C. Moore Collection, bequest of Edward C. Moore, 1891 91.1.463) is courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The photographs of the bell-krater depicting the Hephaistia festival (Fletcher Fund, 1956 56.171.49) are courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The map of Greek dialects in the Classical period (using data from Roger D. Woodard [2008], "Greek dialects", in Roger D. Woodard [ed.], The Ancient Languages of Europe [Cambridge: Cambridge University Press], p.51) is by Future Perfect at Sunrise via Wikimedia Commons.
The photograph of the marble statuette of the Mother of the Gods (Rogers Fund, 1922 22.139.24) is courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The photographs of dining vessels (accession numbers 48.136.2, X.21.33, 23.74, 41.162.244, 41.162.262, 65.78, 1977.11.5, 40.11.24, 41.162.151, 1977.11.4, 07.286.34, 06.1021.105, and 10.210.15) are courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The photograph of The Death of Socrates (1787) by Jacques Louis David (Catharine Lorillard Wolfe Collection, Wolfe Fund, 1931 31.45) is courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The photograph of the hydria depicting women at a fountain-house (Rogers Fund, 1906 06.1021.77) is courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
The photograph of the hydria depicting the abduction of Persephone by Hades (gift of Miss Matilda W. Bruce, 1907 07.128.1) is courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York: www.metmuseum.org.
Created By:
Flyover Zone
Special Thanks:
John McK. Camp, II
Acknowledgements:
The Flyover Zone team dedicates this virtual tour to the memory of Andrew F. Stewart (1948-2023), Professor of the History of Art at the University of California at Berkeley (1979-2019).
- D. Allen, “Imprisonment in Classical Athens.” Classical Quarterly 47.1 (1997): 121-135.
- A. J. Ammerman, “The Eridanos Valley and the Athenian Agora.” American Journal of Archaeology 100.4 (1996): 699-715.
- I. B. Antela-Bernárdez, “Between Medeios and Mithridates: The Peripatetic Constitution of Athens (Agora I 2351).” Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik 171 (2009): 105-108.
- Attic Inscriptions Online https://www.atticinscriptions.com
- V. Azoulay (trans. J. Llloyd), The Tyrant-slayers of Ancient Athens: A Tale of Two Statues. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2017.
- E. P. Baltes, “A Monumental Stepped Statue Base in the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 89.2 (2020): 339-377.
- J. M. Barringer, “A New Approach to the Hephaisteion: Heroic Models in the Athenian Agora,” in P. Schultz and R. von den Hoff (eds.), Structure, Image, Ornament: Architectural Sculpture in the Greek World (Oxford: Oxbow Books, 2009), 105-120.
- S. Beal, “Attack of the Herulians: Disaster Response in 3rd Century Athens,” in M. Auer and C. Hinker (eds.), Roman Settlements and the "Crisis" of the 3rd Century AD (Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag, 2021), 17-30.
- C. Blackwell (ed.), Dēmos: Classical Athenian Democracy, in A. Mahoney and R. Scaife (eds.), The Stoa: A Consortium for Scholarly Publication in the Humanities), January 22, 2023. https://www.stoa.org/demos/
- J. Boardman, Greek Sculpture: The Classical Period. London: Thames and Hudson, 1985.
- A. L. Boegehold, The Athenian Agora XXVIII. The Lawcourts at Athens: Sites, Buildings, Equipment, Procedure, and Testimonia. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1995.
- J. Bollansée, “The Battle of Oinoe in the Stoa Poikile: A Fake Jewel in the Fifth-Century Athenian Crown?” Ancient Society 22 (1991): 91-126.
- D. W. Bradeen, “The Fifth-century Archon List.” Hesperia 32.2 (1963): 187-208.
- O. Broneer, “Notes on Three Athenian Cult Places.” Αρχαιολογική Εφημερίς 99 (1960): 54-67.
- S. J. Burgess, “The Athenian Eleven: Why Eleven?” Hermes 133.3 (2005): 328-336.
- J. M. Camp, “The Agora: Public Life and Administration,” in J. Neils and D. K. Rogers (eds.), The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Athens (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021), 86-97.
- J. M. Camp, "Excavations in the Athenian Agora, 2008-2012." Hesperia 84.3 (2015): 467-513.
- J. M. Camp, “Inscriptions and Public Space in the Agora of Athens,” in W. Eck et al. (eds.), Öffentlichkeit-Monument-Text (XIV Congressus Internationalis Epigraphiae Graecae et Latinae 27.-31. Augusti MMXII: Akten; Berlin: De Gruyter, 2014), 91-104.
- J. M. Camp, The Athenian Agora: Site Guide. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2010.
- J. M. Camp, “Excavations in the Athenian Agora: 2002-2007.” Hesperia 76.4 (2007): 627-663.
- J. M. Camp, The Athenian Agora: A Short Guide to the Excavations. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 16, rev. ed.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2003.
- J. M. Camp, Horses and Horsemanship in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 24.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1998.
- J. M. Camp, The Athenian Agora: Excavations in the Heart of Classical Athens. London: Thames and Hudson, 1986.
- J. M. Camp, Gods and Heroes in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 19.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1980.
- J. M. Camp, The Water Supply of Ancient Athens from 3000 to 86 B.C. Princeton: PhD dissertation, Princeton University, 1977.
- J. M. Camp and W. B. Dinsmoor, Jr., Ancient Athenian Building Methods. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 21.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1984.
- J. M. Camp and J. H. Kroll, “The Agora Mint and Athenian Bronze Coinage.” Hesperia 70.2 (2001): 127-162.
- J. M. Camp and B. Martens, "Recent Excavations in the Athenian Agora, 2013–2019." Hesperia 89.4 (2020): 593-657.
- E. Carawan, The Athenian Amnesty and Reconstructing the Law. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2013.
- E. Carawan, “The Case Against Nikomachos.” Transactions of the American Philological Association 140.1 (2010): 71-95.
- V. A. Champion-Smith, Pausanias in Athens: An Archaeological Commentary on the Agora of Athens. Ph.D. dissertation, University College London, 1998.
- L. Cohn-Haft, “Divorce in Classical Athens.” Journal of Hellenic Studies 115 (1995): 1-14.
- J. J. Coulton, The Architectural Development of the Greek Stoa. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1976.
- H. Craig and V. Craig, "Greek Marbles: Determination of Provenance by Isotopic Analysis." Science N. S. 176.4033 (Apr. 28, 1972): 401-403.
- R. D. Cromey, “Apollo Patroos and the Phratries.” L'antiquité Classique 75 (2006): 41-69.
- M. Crosby, “The Poros Building.” Hesperia 20.3 (1951): 168-187.
- M. Crosby, “The Altar of the Twelve Gods in Athens,” in Commemorative Studies in Honor of Theodore Leslie Shear (Hesperia Supplement 8; Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1949), 82-103 + 447-450.
- A. Delivorrias, “The Sculpted Decoration of the So-Called Theseion: Old Answers, New Questions.” Studies in the History of Art 49 (1997): 82-107.
- B. Develin, “The Battle of Oinoe Meets Ockham's Razor?” Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik 99 (1993): 235-240.
- W. B. Dinsmoor, Observations on the Hephaisteion. (Hesperia Supplement 5.) Amsterdam: Swets & Zeitlinger B. V., 1975.
- W. B. Dinsmoor, “The Internal Colonnade of the Hephaisteion.” Hesperia 37.2 (1968): 159-177.
- W. B. Dinsmoor, “The Monument of Agrippa at Athens.” American Journal of Archaeology 24.1 (1920): 83.
- R. G. Edmonds, "Alcibiades the Profane: Images of the Mysteries in Plato’s Symposium," in P. Destrée and Z. Giannopoulou (eds.), Plato’s Symposium: A Critical Guide (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2017), 194-215.
- C. N. Edmonson, “Onesippos' Herm,” in Studies in Attic Epigraphy, History and Topography Presented to Eugene Vanderpool (Hesperia Supplement 19; Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1982), 48-50 + 212.
- V. Evangelidis, “Agoras and Fora: Developments in the Central Public Space of the Cities of Greece During the Roman Period.” Annual of the British School at Athens 109 (2014): 335-356.
- L. P. Fenger, Dorische Polychromie: Untersuchungen über die Anwendung der Farbe auf dem dorischen Tempel. Berlin: A. Asher & Co., 1886.
- A. Frantz, The Athenian Agora XXIV. Late Antiquity: A.D. 267-700. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1988.
- A. Frantz, The Middle Ages in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 7.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1974.
- L. M. Gadbery, “The Sanctuary of the Twelve Gods in the Athenian Agora: A Revised View.” Hesperia 61.4 (1992): 447-489.
- M. Gagarin, “The Torture of Slaves in Athenian Law.” Classical Philology 91.1 (1996): 1-18.
- L. Gawlinski, “The Athenian Calendar of Sacrifices: A New Fragment from the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 76.1 (2007): 37-55.
- D. J. Geagan, The Athenian Agora XVIII. Inscriptions: The Dedicatory Monuments. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2011.
- D. J. Geagan, The Athenian Constitution after Sulla. (Hesperia Supplement 12.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1967.
- V. R. Grace, Amphoras and the Ancient Wine Trade. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 6, rev. ed.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1979.
- Y. Hamilakis, “Double Colonization: The Story of the Excavations of the Athenian Agora (1924–1931).” Hesperia 82.1 (2013): 153-177.
- E. M. Harris, “Rule of Law and Lawcourts,“ in J. Neils and D. K. Rogers (eds.), The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Athens (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021), 392-404.
- E. B. Harrison, “Aphrodite Hegemone in the Athenian Agora,” in Akten des XIII. Internationalen Kongress für Klassische Archäologie (Deutsches Archäologisches Institut, Berlin 1988; Mainz am Rhein: Verlag Philipp von Zabern, 1990), 346.
- E. B. Harrison, “Alkamenes' Sculptures for the Hephaisteion, Part I: The Cult Statues.” American Journal of Archaeology 81.2 (1977): 137-178.
- E. B. Harrison, “Alkamenes' Sculptures for the Hephaisteion, Part II: The Base.” American Journal of Archaeology 81.3 (1977): 265-287.
- E. B. Harrison, “Alkamenes' Sculptures for the Hephaisteion, Part III: Iconography and Style.” American Journal of Archaeology 81.4 (1977): 411-426.
- E. B. Harrison, The Athenian Agora XI. Archaic and Archaistic Sculpture. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1965.
- E. B. Harrison, Ancient Portraits from the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 5.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1960.
- C. W. Hedrick, Jr., “The Temple and Cult of Apollo Patroos in Athens.” American Journal of Archaeology 92.2 (1988): 185-210.
- N. Herz and W. K. Pritchett, “Marble in Attic Epigraphy.” American Journal of Archaeology 57.2 (1953): 71-83.
- N. Herz and D. B. Wenner, “Stable Isotopic Analysis: A New Tool for the Classical Archaeologist.” Classical Outlook 58.2 (1980-1981): 37-39.
- B. H. Hill, “The Interior Colonnade of the Hephaisteion,” in Commemorative Studies in Honor of Theodore Leslie Shear (Hesperia Supplement 8; Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1949), 190.
- A. T. Hodge, The Woodwork of Greek Roofs. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1960.
- M. B. Hollinshead, "’Adyton,’ ‘Opisthodomos,’ and the Inner Room of the Greek Temple.” Hesperia 68.2 (1999): 189-218..
- S. Hornblower and A. Spawforth (eds.), Oxford Classical Dictionary. 4th ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2012.
- V. Hunter, “The Prison of Athens: A Comparative Perspective.” Phoenix 51.3-4 (1997): 296-326.
- L. H. Jeffery, “The Battle of Oinoe in the Stoa Poikile: A Problem in Greek Art and History.” Annual of the British School at Athens 60 (1965): 41-57.
- K. Jeppesen, Paradeigmata: Three Mid-Fourth Century Main Works of Hellenic Architecture, Reconsidered. (Jutland Archaeological Society Publications Vol. IV) Aarhus: Aarhus University Press, 1958.
- S. Karouzou, “Alkamenes und das Hephaisteion.” Athenische Mitteilungen 69-70 (1954/1955): 67-94.
- N. Kaye, “The Dedicatory Inscription of the Stoa of Attalos in the Athenian Agora: Public Property, Commercial Space, and Hellenistic Kings.” Hesperia 85.3 (2016): 537-558.
- M. L. Keller, “The Eleusinian Mysteries of Demeter and Persephone: Fertility, Sexuality, and Rebirth.” Journal of Feminist Studies in Religion 4.1 (1988): 27-54.
- C. Kerényi (trans. R. Manheim), Eleusis: Archetypal Image of Mother and Daughter. (Bollingen Series LXV.4.) Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1967.
- F. S. Kleiner, Greek and Roman Coins in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 15.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1975.
- H. Knell, “Der jüngere Tempel des Apollon Patroos auf der Athener Agora.” Jahrbuch des Deutschen Archäologischen Instituts 109 (1994): 217-237.
- H. Koch, Studien zum Theseustempel in Athen. (Abhandlungen der Sachsischen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Leipzig, phil.-hist. Klasse 47.2.) Berlin: Akademie Verlag, 1955.
- G. V. Lalonde, “A Hero Shrine in the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 49.1 (1980): 97-105.
- G. V. Lalonde, “A Fifth Century Hieron Southwest of the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 37.2 (1968): 123-133.
- G. V. Lalonde, M. K. Langdon, and M. B. Walbank, The Athenian Agora XIX. Inscriptions: Horoi, Poletai Records, and Leases of Public Lands. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1991.
- S. Lambert, “British Museum: Decrees of the Council and Assembly.” Attic Inscriptions in UK Collections 4.2 (2020).
- S. D. Lambert, “The Sacrificial Calendar of Athens.” Annual of the British School at Athens 97 (2002): 353-399.
- J. L. Lamont, “The Curious Case of the Cursed Chicken: A New Binding Ritual from the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 90.1 (2021): 79-113.
- M. Lang, Life, Death and Litigation in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 23.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1994.
- M. Lang, The Athenian Agora XXV. Ostraka. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1990.
- M. Lang, Graffiti in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 14, rev. ed.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1988.
- M. Lang, Socrates in the Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 17.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1978.
- M. Lang, The Athenian Agora XXI. Graffiti and Dipinti. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1976.
- M. Lang, Waterworks in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 11.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1968.
- M. Lang and J. M. Camp, The Athenian Citizen: Democracy in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 4, rev. ed.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2004.
- M. Lang and M. Crosby, The Athenian Agora X. Weights, Measures, and Tokens. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1964.
- M. L. Lawall, “The Archaeology of Markets and Trade,” in J. Neils and D. K. Rogers (eds.), The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Athens (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021), 244-256.
- M. L. Lawall, “The Temple of Apollo Patroos Dated by an Amphora Stamp.” Hesperia 78 (2009): 387-403.
- C. Lawton, Marbleworkers in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 27.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2006.
- D. Leão, “The Eleusinian Mysteries and Political Timing in the Life of Alcibiades,” in L. Roig Lanzillotta and I. Muñoz Gallarte (eds.), Plutarch in the Religious and Philosophical Discourse of Late Antiquity (Leiden: Brill, 2012), 181-192.
- S. Leigh, “The Monumental Fountain in the Athenian Agora: Reconstruction and Interpretation,” in G. A. Aristodemou and T. P. Tassios (eds.), Great Waterworks in Roman Greece. Aqueducts and Monumental Fountain Structures: Function in Context (Oxford: Archaeopress, 2018), 218-234.
- P. Liddel, “The Places of Publication of Athenian State Decrees from the 5th Century BC to the 3rd Century AD.” Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik 143 (2003): 79-93.
- R. D. Luginbill, “The Battle of Oinoe, the Painting in the Stoa Poikile, and Thucydides’ Silence.” Historia 63.3 (2014): 278-292.
- M. MacKinnon, “Animals, Economics, and Culture in the Athenian Agora: Comparative Zooarchaeological Investigations.” Hesperia 83.2 (2014): 189-255.
- S. L. Martin-Mcauliffe and J. K. Papadopoulos, “Framing Victory: Salamis, the Athenian Acropolis, and the Agora.” Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians 71.3 (2012): 332-361.
- A. P. Matthaiou, “Adoption of the Ionic Alphabet in Attica,” in G. K. Giannakis (ed.), Encyclopedia of Ancient Greek Language and Linguistics (Leiden: Brill, 2013). Consulted online on 28 November 2022 <http://dx.doi.org/10.1163/2214-448X_eagll_COM_00000126>
- C. C. Mattusch, Bronzeworkers in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 20.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1982.
- B. D. Meritt, “Perikles, the Athenian Mint, and the Hephaisteion.” Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 119.4 (1975): 267-274.
- B. D. Meritt, Inscriptions from the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 10.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1966.
- B. D. Meritt, “Greek Inscriptions.” Hesperia 5.3 (1936): 355-430.
- B. D. Meritt and J. S. Traill, The Athenian Agora XV. Inscriptions: The Athenian Councillors. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1974.
- L. S. Meritt, “Some Ionic Architectural Fragments from the Athenian Agora,” in Studies in Athenian Architecture, Sculpture and Topography Presented to Homer A. Thompson (Hesperia Supplement 20; Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1982), 82-92.
- L. S. Meritt, “The Stoa Poikile.” Hesperia 39.4 (1970): 233-264.
- E. A. Meyer, “Athenian Inscriptions,” in J. Neils and D. K. Rogers (eds.), The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Athens (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021), 98-109.
- M. M. Miles, The Athenian Agora XXXII. The City Eleusinion. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1998.
- M. M. Miles and J. Neils, “Athenian Festivals,” in J. Neils and D. K. Rogers (eds.), The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Athens (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021), 332-344.
- D. C. Mirhady and C. Schwarz, “Dikastic Participation.” Classical Quarterly N. S. 61.2 (2011): 744-748.
- C. H. Morgan, “The Sculptures of the Hephaisteion III. The Pediments, Akroteria and Cult Images.” Hesperia 32.1 (1963): 91-108.
- C. H. Morgan, “The Sculptures of the Hephaisteion II. The Friezes.” Hesperia 31.3 (1962): 221-235.
- C. H. Morgan, “The Sculptures of the Hephaisteion I.” Hesperia 31.2 (1962): 210-219.
- G. E. Mylonas, “Eleusis and the Eleusinian Mysteries.” The Classical Journal 43.3 (1947): 130-146.
- J. Neils and S. V. Tracy, The Games at Athens. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 25.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2003.
- M. Nelson, “The Phantom Stelai of Lysias, Against Nicomachus 17.” Classical Quarterly N. S. 56.1 (2006): 309-312.
- J. Paga, “The Southeast Fountain House in the Athenian Agora: A Reappraisal of Its Date and Historical Context.” Hesperia 84.2 (2015): 355-387.
- A. Painesi, “Historical Events as a Means of Iconographic Interpretation: The Reconstruction of Lost Greek Historical Paintings of the Fifth and Fourth Centuries B.C.” Cahiers d’Histoire 31.2 (2013): 157-179.
- O. Palagia, “The Painted Battle of Oinoe in the Stoa Poikile and the Events of 506 B.C.,” in J. Fouquet et al. (eds.), Argonautica. Festschrift für Reinhard Stupperich (Boreas Beiheft 12; Marsberg/Padberg: Münstersche Beiträge zur Archäologie, 2018), 61-65.
- J. K. Papadopoulos and M. R. Schilling, Ceramicus Redivivus: The Early Iron Age Potters' Field in the Area of the Classical Athenian Agora. (Hesperia Supplement 31.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2003.
- J. K. Papadopoulos and E. L. Smithson, “The Cultural Biography of a Cycladic Geometric Amphora: Islanders in Athens and the Prehistory of Metics.” Hesperia 71.2 (2002): 149-199.
- C. Picard, “Le complexe Métrôon-Bouleutérion-Prytanikon, à l’Agora d’Athènes.” Revue Archéologique 12 (1938): 97-101.
- D. Plantzos, review of S. Dumont, Vrysaki: A Neighborhood Lost in Search of the Athenian Agora. Bryn Mawr Classical Review 2022.01.11, https://bmcr.brynmawr.edu/2022/2022.01.11/.
- A. J. Podlecki, “The Political Significance of the Athenian ‘Tyrannicide’-Cult.” Historia 15.2 (1966): 129-141.
- R. L. Pounder, “A Hellenistic Arsenal in Athens.” Hesperia 52.3 (1983): 233-256.
- P. Probert, “Phonology,” in E. J. Bakker (ed.), A Companion to the Ancient Greek Language (Chichester: Blackwell, 2010), 85-103.
- P. J. Rhodes, The Athenian Constitution Written in the School of Aristotle. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press, 2017.
- P. J. Rhodes, “Public Documents in the Greek States: Archives and Inscriptions, Part I.” Greece & Rome 48.1 (2001): 33-44.
- P. J. Rhodes, “Public Documents in the Greek States: Archives and Inscriptions, Part II.” Greece & Rome 48.2 (2001): 136-153.
- N. Robertson, “The City Center of Archaic Athens.” Hesperia 67.3 (1998): 283-302.
- N. Robertson, “The Laws of Athens, 410-399 BC: The Evidence for Review and Publication.” Journal of Hellenic Studies 110 (1990): 43-75.
- S. I. Rotroff, Industrial Religion: The Saucer Pyres of the Athenian Agora. (Hesperia Supplement 47.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2013.
- S. I. Rotroff, “An Anonymous Hero in the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 47.2 (1978): 196-209.
- S. I. Rotroff and R. D. Lamberton, Women in the Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 26.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 2005.
- S. I. Rotroff and J. H. Oakley, Debris from a Public Dining Place in the Athenian Agora. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1992.
- I. Rutherford, “Canonizing the Pantheon: The Dodekatheon in Greek Religion and Its Origins,” in J. N. Bremmer and A. Erskine (eds.), The Gods of Ancient Greece: Identities and Transformations (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2013), 43-54.
- B. Sauer, Das sogennante Theseion und sein plastischer Schmuck. Leipzig: Giesecke & Devrient, 1899.
- J. H. Schreiner, “The Battle of Oinoe: A Totally Intractable Problem?” Echos du monde classique/Classical Views 37 (n.s. 12) No. 1 (1993): 25-28.
- F. Seiler, Die Griechische Tholos: Untersuchungen Zur Entwicklung, Typologie und Funktion Kunstmässiger Rundbauten. Mainz am Rhein: Verlag Philipp von Zabern, 1986.
- H. A. Shapiro, “#Leagros: An Athenian Life,” in J. Neils and D. K. Rogers (eds.), The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Athens (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021), 7-17.
- J. L. Shear, Serving Athena. The Festival of the Panathenaia and the Construction of Athenian Identities. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021.
- J. L. Shear, “The Tyrannicides, Their Cult and the Panathenaia: A Note.” Journal of Hellenic Studies 132 (2012): 107-119.
- T. L. Shear, “The Campaign of 1934.” Hesperia 4.3 (1935): 340-370.
- T. L. Shear, Jr., Trophies of Victory: Public Building in Periklean Athens. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 2016.
- T. L. Shear, Jr., “The Persian Destruction of Athens: Evidence from Agora Deposits.” Hesperia 62.4 (1993): 383-482.
- T. L. Shear, Jr., “The Athenian Agora: Excavations of 1980-1982.” Hesperia 53.1 (1984): 1–57.
- T. L. Shear, Jr., “The Athenian Agora: Excavations of 1973-1974.” Hesperia 44.4 (1975): 331-374.
- T. L. Shear, Jr., “The Athenian Agora: Excavations of 1971.” Hesperia 42.2 (1973): 121-179.
- T. L. Shear, Jr., “The Athenian Agora: Excavations of 1970.” Hesperia 40.3 (1971): 241-279.
- T. L. Shear, Jr., “The Monument of the Eponymous Heroes in the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 39.3 (1970): 145-222.
- B. B. Shefton, “Some Iconographic Remarks on the Tyrannicides.” American Journal of Archaeology 64.2 (1960): 173-179.
- J. P. Sickinger, “New Ostraka from the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 86.3 (2017): 443-508.
- R. Sing, “The Rates of Jury Pay and Assembly Pay in Fourth-century Athens.” Classical Quarterly 71.1 (2021): 119-134.
- G. P. Stevens, “Some Remarks upon the Interior of the Hephaisteion.” Hesperia 19.3 (1950): 143-164.
- G. P. Stevens, “Grilles of the Hephaisteion.” Hesperia 19.3 (1950): 165-173.
- G. P. Stevens, “A Tile Standard in the Agora of Ancient Athens.” Hesperia 19.3 (1950): 174-188.
- G. P. Stevens, “The Ceiling of the Opisthodomus of the Theseum.” American Journal of Archaeology 15.1 (1911): 18-23.
- A. Stewart, "'Memorials of All Our Noble Deeds.' Politics, Power, and Representation in the Athenian Agora, 510 B.C. to A.D. 14: A Critical Review." Hesperia 92.3 (2023): 191-310.
- A. Stewart, “The Sculptures of the Temple of Ares in the Agora: Discoveries Old and New,” in J. Neils and O. Palagia (eds.), From Kallias to Kritias: Art in Athens in the Second Half of the Fifth Century B.C. (Berlin/Boston: Walter de Gruyter, 2022), 197-216.
- A. Stewart, “Notes on the Origins and Early Development of the ‘Agora of the Kerameikos’,” in C. M. Draycott et al. (eds.), Visual Histories of the Classical World. Essays in Honour of R.R.R. Smith (Turnhout: Brepols, 2018), 299-308.
- A. Stewart, “Classical Sculpture from the Athenian Agora, Part 1: The Pediments and Akroteria of the Hephaisteion.” Hesperia 87.4 (2018): 681-741.
- A. Stewart, “Hellenistic Sculpture from the Athenian Agora, Part 4: The East Pediment and Akroteria of the Temple of Apollo Patroos.” Hesperia 86.2 (2017): 273-323.
- A. Stewart, “Hellenistic Freestanding Sculpture from the Athenian Agora, Part 1: Aphrodite.” Hesperia 81.2 (2012): 267-342.
- A. Stewart, “Hellenistic Freestanding Sculpture from the Athenian Agora, Part 2: Demeter, Kore, and the Polykles Family.” Hesperia 81.4 (2012): 655-689.
- A. Stewart, B. Frischer, and M. Abdelaziz, “Fear and Loathing in the Hellenistic Agora: Antenor's Tyrannicides Return.” Hesperia 91.2 (2022): 311-350.
- A. Stewart et al., “Classical Sculpture from the Athenian Agora, Part 3: The Pediments, Metopes, and Akroteria of the Temple of Ares (Temple of Athena Pallenis).” Hesperia 90.3 (2021): 533-604.
- A. Stewart et al., “Classical Sculpture from the Athenian Agora, Part 2: The Friezes of the Temple of Ares (Temple of Athena Pallenis).” Hesperia 88.4 (2019): 625-705.
- V. M. Strocka, “Die Komposition deri Tyrannenmōrdergruppe.” Münchner Jahrbuch der bildenden Kunst LXXII.3 (2021): 7-33.
- J. Stroszeck, “Water and Water Management,” in J. Neils and D. K. Rogers (eds.), The Cambridge Companion to Ancient Athens (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021), 110-123.
- J. Stuart and N. Revett, The Antiquities of Athens, volume 3. London: John Nichols, 1794.
- J. P. Sturm, “The Afterlife of the Hephaisteion: The Interpretatio Christiana of an Ancient Athenian Monument.” Hesperia 85.4 (2016): 795-825.
- D. Sudjic, Stalin's Architect: Power and Survival in Moscow. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2022.
- J. B. Summitt, Greek Architectural Polychromy from the Seventh to Second Centuries B.C.: History and Significance. Ann Arbor: PhD dissertation, University of Michigan, 2000.
- J. G. Taylor, “Oinoe and the Painted Stoa: Ancient and Modern Misunderstandings?” American Journal of Philology 119.2 (1998): 223-243.
- D. A. Teegarden, “The Oath of Demophantos, Revolutionary Mobilization, and the Preservation of the Athenian Democracy.” Hesperia 81.3 (2012): 433-465.
- D. B. Thompson, An Ancient Shopping Center: The Athenian Agora. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 12, rev. ed.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1993.
- D. B. Thompson, “The Garden of Hephaistos.” Hesperia 6.3 (1937): 396-425.
- D. B. Thompson and R. E. Griswold, Garden Lore of Ancient Athens. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 8.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1982.
- H. A. Thompson, The Stoa of Attalos II in Athens. (Excavations of the Athenian Agora Picture Book No. 2, rev. ed.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1992.
- H. A. Thompson, “Activity in the Athenian Agora: 1966-1967.” Hesperia 37.1 (1968): 36-72.
- H. A. Thompson, “Activity in the Athenian Agora 1960-1965.” Hesperia 35.1 (1966): 37-54.
- H. A. Thompson, “The Sculptural Adornment of the Hephaisteion.” American Journal of Archaeology 66.3 (1962): 339-347.
- H. A. Thompson, 1961 Season’s Report for Section K. Unpublished Excavation Report, 1961.
- H. A. Thompson, “Activities in the Athenian Agora: 1954.” Hesperia 24.1 (1955): 50-71.
- H. A. Thompson, “Excavations in the Athenian Agora: 1952.” Hesperia 22.1 (1953): 25-56.
- H. A. Thompson, “Excavations in the Athenian Agora: 1951.” Hesperia 21.2 (1952): 83-113.
- H. A. Thompson, “The Altar of Pity in the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 21.1 (1952): 47-82.
- H. A. Thompson, “Excavations in the Athenian Agora: 1949.” Hesperia 19.4 (1950): 313-337.
- H. A. Thompson, The Tholos of Athens and Its Predecessors. (Hesperia Supplement 4.) Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1940.
- H. A. Thompson, “Buildings on the West Side of the Agora.” Hesperia 6.1 (1937): 1.
- H. A. Thompson and R. E. Wycherley, The Athenian Agora XIV. The History, Shape, and Uses of an Ancient City Center. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1972.
- W. E. Thompson, “The Inscriptions in the Hephaisteion.” Hesperia 38.1 (1969): 114-118.
- R. F. Townsend, The Athenian Agora XXVII. The East Side of the Agora: The Remains Beneath the Stoa of Attalos. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1995.
- J. Travlos, Pictorial Dictionary of Ancient Athens. London: Thames and Hudson, 1971.
- B. Tsakirgis, “Living and Working Around the Athenian Agora: A Preliminary Case Study of Three Houses,” in B. A. Ault and L. C. Nevett (eds.), Ancient Greek Houses and Households: Chronological, Regional, and Social Diversity (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 2005), 67-82.
- E. Vanderpool, “The State Prison of Athens,” in K. DeVries (ed.), From Athens to Gordion: The Papers of a Memorial Symposium for Rodney S. Young (University Museum Papers 1; Philadelphia: The University Museum, University of Pennsylvania, 1980), 17-31.
- E. Vanderpool, “Metronomoi.” Hesperia: 37.1 (1968): 73-76.
- E. Vanderpool, “Athens Honors the Emperor Tiberius.” Hesperia 28.1 (1959): 86-90.
- E. Vanderpool, “The Route of Pausanias in the Athenian Agora.” Hesperia 18.1 (1949): 128-137.
- E. Vanderpool, “Tholos and Prytanikon.” Hesperia 4.3 (1935): 470-475.
- F. W. Walbank et al. (eds.), The Cambridge Ancient History Vol. VII Part 1: The Hellenistic World. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1984.
- A. G. Woodhead, The Athenian Agora XVI. Inscriptions: The Decrees. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1997.
- W. F. Wyatt, Jr. and C. N. Edmonson, “The Ceiling of the Hephaisteion.” American Journal of Archaeology 88.2 (1984): 135-167.
- R. E. Wycherley, “The Stones of Athens.” Greece & Rome 21.1 (1974): 54-67.
- R. E. Wycherley, The Athenian Agora III. Literary and Epigraphical Testimonia. Princeton: American School of Classical Studies at Athens, 1957.
- M. Yeroulanou, “Metopes and Architecture: The Hephaisteion and the Parthenon.” Annual of the British School at Athens 93 (1998): 401-425.

Subscribe to our Newsletter
Receive updates and exclusive promotions from Flyover Zone






